- Eng
- Deu
- Fra
How to Choose the Best Waste Pump for Your Needs and Avoid Common Mistakes
Choosing the right waste pump for your needs can be a daunting task, especially with the variety of options available on the market today. A waste pump is essential for efficiently transferring wastewater and can be a crucial component in a variety of applications, from residential settings to industrial environments. Understanding the specific requirements of your situation can make a significant difference in selecting a pump that not only meets your needs but also operates efficiently and effectively.
As you navigate the selection process, it's important to consider factors such as the type of waste being handled, the required flow rate, and the lift height. Many users fall into common pitfalls, such as underestimating the power needed or overlooking the importance of materials suited for specific waste types. By being aware of these mistakes, you can make informed choices that prevent unnecessary complications and expenses in the future. Ultimately, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to choose the best waste pump that aligns with your needs while avoiding the typical errors that many make during the selection process.

Understanding the Different Types of Waste Pumps Available on the Market
When selecting a waste pump, understanding the different types available is essential for meeting specific needs effectively. There are primarily three types of waste pumps: submersible pumps, centrifugal pumps, and diaphragm pumps. Submersible pumps are designed to operate while submerged in the liquid, making them suitable for wastewater and sewage applications. According to industry reports, submersible pumps account for approximately 60% of the sewage pump market due to their efficiency and compact size. Conversely, centrifugal pumps, which use rotational energy to move fluids, are typically employed in industrial settings where higher flow rates are necessary. These pumps are favored for their reliability, especially in applications that require high-pressure output.
Diaphragm pumps operate using a flexible membrane, making them ideal for handling sludges, slurries, and highly viscous materials. Their ability to handle solids and various chemical compositions makes them a preferred choice in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to food processing. Research from the Fluid Sealing Association highlights that diaphragm pumps are increasingly adopted in environments where contamination is a concern, constituting about 15% of the overall waste pump market share. Each type of pump comes with its own set of advantages and limitations, making it crucial to identify the specific operational demands before making a purchase. Understanding these distinctions not only aids in selecting the right pump but also helps in avoiding common pitfalls that can arise from mismatched applications.
How to Choose the Best Waste Pump for Your Needs and Avoid Common Mistakes - Understanding the Different Types of Waste Pumps Available on the Market
| Type of Waste Pump | Best Suited For | Flow Rate (GPM) | Maximum Lift (Feet) | Power Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Submersible Pump | Flooded areas, sewage drainage | 30 - 150 GPM | 20 - 30 feet | Electric |
| Transfer Pump | Moving water from one area to another | 50 - 200 GPM | 10 - 30 feet | Gasoline or Electric |
| Sewage Pump | Pumping sewage and solids | 40 - 120 GPM | 15 - 25 feet | Electric |
| Effluent Pump | Gray water treatment | 20 - 60 GPM | 10 - 15 feet | Electric |
| Drum Pump | Thicker liquids, sludge | 10 - 30 GPM | Varies based on design | Manual or Electric |
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Waste Pump for Specific Uses
When selecting a waste pump, understanding the specific requirements of your application is crucial. Common factors to consider include pump capacity, the type of waste being handled, and the power source. For instance, a report from the Waste Equipment Manufacturers Association indicates that the average capacity needed for residential pumping of wastewater can range from 1,500 to 2,500 gallons per hour, while industrial settings may require significantly more. It's essential to match the pump’s specifications with the demands of your situation to ensure efficient operation and longevity.
Tip: Always evaluate the solid size your pump can handle. Many waste pumps have limitations on the size of solids they can process, so understanding these limits can prevent clogs and operational failures. If handling large debris is necessary, consider pumps designed for such tasks, as they can significantly reduce maintenance needs and operational downtime.
Another critical factor is the environment in which the pump will operate. For example, pumps used in highly corrosive environments require materials that can withstand severe conditions, as outlined in studies by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. Evaluating the surrounding conditions and selecting the right materials can save on replacement costs and enhance pump performance over time.
Tip: Regular maintenance checks can identify potential issues early on, extending the life of your waste pump. Create a routine schedule to inspect your pump, ensuring any wear and tear is addressed promptly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Purchasing a Waste Pump
When purchasing a waste pump, it's crucial to be aware of common mistakes that can lead to inefficiency and additional costs. One major pitfall is underestimating the flow rate required for your specific application. According to industry reports, a significant number of users fail to consider the volume of waste that needs to be handled, which can lead to selecting a pump that is either overpowered or underpowered. Understanding the required gallons per minute (GPM) is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature wear and tear on the equipment.
Another common mistake is overlooking the importance of head lift capabilities. Many buyers focus solely on the pump's horsepower without taking into account the height to which the waste must be lifted. Insufficient head lift can result in operational inefficiencies or complete system failures. Industry studies suggest that nearly 30% of waste pump users face operational challenges because they did not correctly assess their head lift requirements before making a purchase.
Tip: Always calculate both the flow rate and head lift prior to purchasing a waste pump to ensure compatibility with your application needs.
In addition, failure to consider the pump's material composition can lead to problems with durability and longevity. For instance, pumps made from unsuitable materials may corrode or degrade when exposed to harsh waste substances, resulting in costly repairs or replacement. Reports indicate that investing in a waste pump with the right material for your specific waste type can extend the lifespan of the equipment by up to 50%.
Tip: Review the material specifications carefully and match them to the type of waste your pump will handle to avoid premature failure.
Maintenance Tips to Extend the Life of Your Waste Pump
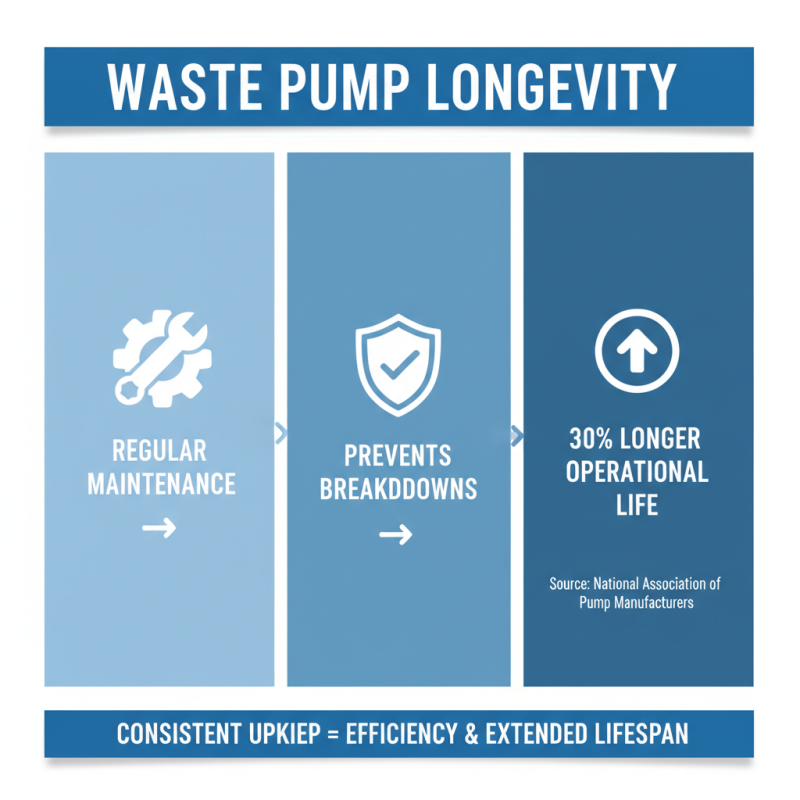
When selecting a waste pump, maintenance plays a critical role in ensuring its longevity and efficiency. Regular maintenance not only prevents unexpected breakdowns but also extends the lifespan of the equipment. According to a study by the National Association of Pump Manufacturers, proper maintenance can increase the operational life of pumps by up to 30%. This finding underscores the importance of adhering to a consistent upkeep schedule.
One essential tip for maintaining your waste pump is to regularly inspect and clean the intake screen. Accumulation of debris can restrict flow and lead to overheating, damaging internal components. Additionally, monitoring the fluid levels and ensuring they’re within the manufacturer’s specified range can prevent the pump from running dry—a common issue that can severely affect performance.
Furthermore, consider implementing a scheduled lubrication routine for moving parts. Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, resulting in a smoother operation. In fact, a report from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicates that regular lubrication can reduce component wear by 40%. By taking these proactive measures, you can ensure that your waste pump remains efficient and reliable for years to come.
How to Properly Install and Operate Your Waste Pump for Optimal Performance
Proper installation and operation of your waste pump are crucial for achieving optimal performance. Before beginning the installation process, ensure you have all necessary tools and read the manufacturer's guidelines thoroughly. Choose a location that allows for easy access while ensuring the pump is positioned below the wastewater source to facilitate better flow. Pay attention to the alignment of the inlet and outlet pipes, making sure they are securely connected and free from any potential obstructions.
During operation, it's essential to monitor the pump for any unusual noises or vibrations that may indicate underlying issues. Regular maintenance, including checking for blockages and inspecting seals, can significantly prolong the life of your waste pump. Be mindful of the materials being pumped; only allow appropriate waste to pass through, as improper items can easily clog or damage the system. By adhering to these practices, you can ensure your waste pump operates efficiently and reliably for years to come.
Related Posts
-

Understanding Waste Pumps How They Work and Their Importance in Modern Waste Management
-
What is Vacuum Oil and How it Benefits Industrial Applications
-

How to Effectively Pump Oil for Maximum Efficiency and Safety
-

2025 Top Vacuum Oil Types: Key Benefits and Uses You Should Know
-
Understanding the Efficiency and Applications of Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps in Modern Industries
-

2025 Top 5 Suction Pumps: Best Picks for Efficiency and Reliability
